Welche Vorteile bieten Assistenzsysteme?
Die Vierte Industrielle Revolution, auch bekannt als Industrie 4.0, ist derzeit ein viel diskutiertes Thema. Die Digitalisierung und Vernetzung von Produktionsprozessen eröffnen neue Möglichkeiten zur Steigerung von Produktivität und Flexibilität. Mit der zunehmenden Komplexität technischer Lösungen steigen auch die Anforderungen an Mitarbeiter in Industrie- und Handwerksbetrieben. Neue Technologien ermöglichen es den Mitarbeitern, auf innovative Weise mit Maschinen zu interagieren und zusammenzuarbeiten. Moderne Assistenzsysteme bieten vielfältige Unterstützung und entlasten sowohl kognitiv als auch körperlich. Durch diese Systeme können Fehlerquoten und Arbeitsbelastungen reduziert und die Mitarbeiterzufriedenheit verbessert werden. Die Unterstützung durch Assistenzsysteme kann in drei Kategorien eingeteilt werden.
- Steigerung der Effizienz am Arbeitsplatz: Der Mitarbeiter erhält vom Assistenzsystem zusätzliche physische oder mentale Unterstützung, um Aufgaben noch effizienter zu erledigen.
- Förderung der Arbeitsplatzergonomie: Das Arbeitssystem erleichtert die Arbeit für den Angestellten und ermöglicht eine sichere und ergonomische Ausführung von Aufgaben.
- Ausgleich von Einschränkungen: Ältere Mitarbeiter oder Mitarbeiter mit Behinderungen können durch den Einsatz von technischen Hilfsmitteln und Assistenzsystemen effektiv in die Arbeitsumgebung eingebunden werden.
Kognitive Assistenzsysteme
Zu den kognitiven Assistenzsystemen gehören moderne Technologien wie Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR) und Mixed Reality (MR). Diese flexiblen Technologien finden bereits heute in vielen Assistenzszenarien Anwendung.
Klassische Werkerassistenzsysteme per Bildschirm, Touchscreen oder Display
Werkerassistenzsysteme spielen eine immer wichtigere Rolle in der Produktion, Montage und Fertigung. Diese intelligenten Systeme unterstützen die Mitarbeiter bei ihrer täglichen Arbeit und tragen dazu bei, die Effizienz und Qualität der Produktion zu steigern. Eine zentrale Komponente dieser Systeme sind die Bildschirme und Touchscreens, die den Mitarbeitern eine intuitive Interaktion ermöglichen.
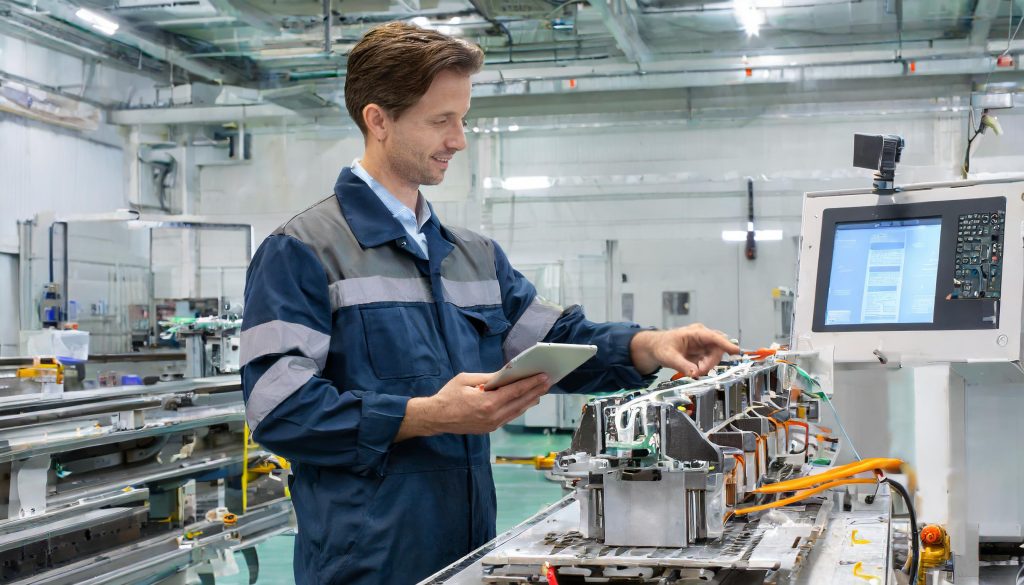

Werker Assistenzsystem an einer Montagelinie
In der modernen Fertigung kommen verschiedene Arten von Bildschirmen und Touchscreens zum Einsatz. Diese reichen von einfachen Monitoren über robuste Industrie-Touchscreens bis hin zu hochwertigen HMI-Touchscreens. Die Wahl des richtigen Bildschirms hängt von den Anforderungen der jeweiligen Anwendung ab. Besonders in der Produktion und Montage ist die Interaktion mit den Bildschirmen über Touchscreens sehr häufig. Mitarbeiter können durch einfaches Berühren des Bildschirms Aktionen ausführen, Parameter ändern oder Informationen abrufen. Dadurch wird die Bedienung der Werkerassistenzsysteme äußerst benutzerfreundlich und intuitiv.
Welchen Inhalt können Assistenzsysteme darstellen?
Neben typischen textbasierten Anweisungen, spielt heutzutage der visuell aufbereitete Informationstransfer eine bedeutende Rolle. Man denke nur an Sprachbarrieren, die mihilfe von einfachen Piktogrammen einfach überwunden werden können. Einige weitere Beispiele für den Einsatz von digitalen Assistenz Systemen:
- Zeichnungen, Materiallisten, Arbeits- und Prüfpläne sowie allgemeine Informationen wie Kantinenpläne oder Unfallverhütungsvorschriften (UVV) und viele andere PDF-Dokumente werden direkt am Montageplatz mehrsprachig angezeigt.
- Komplexe, variantenreiche Endprodukte können mittels übersichtlicher schrittweiser Montageanleitungen bequem montiert werden. die Einbindung von Montagevideos erleichtert nochmals die Übermittlung von Wissen und Information.
- Grafischen Editoren mit verschiedenen Grafikwidgets wie Bildern, Videos, Checklisten, PDF-Anzeigen, Textblöcken und vielem mehr, werden genutzt, um Feedback zu Arbeitsabläufe zu geben und die Prozesse im sinne eines lebendigen Qualitätsmanagementsystem kontinuierlich zu verbessern (Plan – Do – Check – Act = PDCA Zyklus)
- Arbeitsabläufe einzelnerArbeitsstationen können meist per per Drag-and-Drop am Touchscreen ausgewählt und bei Bedarf verschoben werden. Eine optimale Feinplanung und Auslastung der Fertigungskapazitäten, als auch die einfach Erfassung von IST-Zeiten wird ermöglicht
- Lückenlose Dokumentation des Herstellungsprozess für Qualitätsnachweise und als Grundlage für Produktionsverbesserungen. ISO 9001 und IATF16949 normkonform.
- Integration von Prüf- und Maschinendaten Sie Schnittstellen in die Maschinenumgebung, um Prüf- und Maschinendaten in die digitale Assistenzlösung zu integrieren. Arbeitsabläufe können über Maschinensignale abgeschlossen werden, wie zum Beispiel Qualitätsprüfungen bei Endmontagen
- Zeigen Sie allgemeine Unternehmensmeldungen, wie Neueinstellungen, Firmenevents, Erfolge, Umsatzzahlen und den Status aller Arbeitsstationen an den einzelnen Montagestationen an. Direkte unmittelbare Integration in das Shopfloor Management System.

Schutz der teuren Displays, Bildschirme und Touchscreens
Um die teuren HMI-Touchscreens vor Kratzern und Beschädigungen zu schützen, empfiehlt es sich, hochwertige Displayschutzfolien oder enorm robustes Hybridglas zu verwenden. Diese Schutzfolien, respektive Hybridgläser, bieten einen zuverlässigen Schutz vor Kratzern, Schmutz und Stößen. Zusätzlich dazu reduzieren die matten und entspiegelnden Varianten störende Spiegelungen auf den Displays, was gerade bei hellem Umgebungslicht von Vorteil ist. Die Augen der Werker ermüden nicht mehr und das Ablesen wichtiger Informationen für den nächsten Montageschritt oder Arbeitsgang ist ermüdungsfrei möglich.
Erhöhung der Lebensdauer und Mitarbeiterzufriedenheit
Der Einsatz von Displayschutzfolien oder Hybridglas erhöht nicht nur die Lebensdauer der Geräte, sondern steigert auch die Mitarbeiterzufriedenheit. Durch den Schutz der Bildschirme werden teure Reparaturen vermieden und Ausfallzeiten minimiert. Mitarbeiter können sich somit voll und ganz auf ihre Aufgaben konzentrieren, ohne sich um die Sicherheit der Touchscreens sorgen zu müssen.
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass die Interaktion in aller Regel mit den Bildschirmen erfolgt. Häufig über Touchscreens, die eine intuitive Bedienung ermöglichen. Der Einsatz von Displayschutzfolien oder Hybridglas bietet einen effektiven Schutz vor Kratzern und Beschädigungen, erhöht die Lebensdauer der Geräte und steigert die Zufriedenheit der Mitarbeiter.
Lebensdauer elektronischer Displays ausgestattet MIT Displayschutz
VR-Systeme
VR-Systeme (Virtual Reality) ermöglichen es Mitarbeitern, in komplett virtuelle Welten einzutauchen. Dadurch können beispielsweise Schulungen an nicht vorhandenen Geräten durchgeführt oder gefährliche Situationen risikofrei simuliert werden. Solche Systeme sind seit vielen Jahren ein fester Bestandteil der Pilotenausbildung in Flugsimulatoren.
AR-Systeme
AR-Systeme (Augmented Reality) erweitern hingegen die Wahrnehmung der realen Welt durch zusätzliche Informationen. Sie reichen von einfachen Pick-by-Light-Systemen, die Mitarbeiter bei der Montage zu den benötigten Teilen führen, bis hin zu digitalen Projektionssystemen, die Montageanweisungen dynamisch auf Arbeitsflächen projizieren oder mobile Datenbrillen, die nützliche Informationen wie Teilenummern, Maschinen- und Anlagenzustände direkt im Sichtfeld anzeigen können. Sie können auch verwendet werden, um den Benutzer zu einem bestimmten Ort zu führen, beispielsweise in einem Lager.
MR-Systeme
Schließlich vereint MR (Mixed Reality) beide Konzepte und ermöglicht die Erstellung interaktiver virtueller Objekte in der realen Welt. Benutzer können beispielsweise Wartungstechniker sein, die vor Ort ein 3D-Modell der zu reparierenden Maschine zur Verfügung haben, oder Installateure, die die geplante Position der einzubauenden Teile direkt anzeigen oder überlagern können. MR findet auch Anwendung in der Planungs- und Designphase, da es ermöglicht, virtuelle Objekte an einem realen Ort einzufügen und ihre Auswirkungen direkt zu testen. Dies ist besonders vorteilhaft für die Arbeitsplatzplanung. Durch verbesserte Sensortechnik wird es zudem immer einfacher, Standort-, Form- oder Oberflächenmerkmale in diesen Bereichen zu erfassen und somit Dokumentation und Qualitätskontrolle nahtlos in den Arbeitsablauf zu integrieren.
Physische Assistenzsysteme
Aktive Exoskelette
Eine alternative Form der Unterstützung bieten physische Assistenzsysteme, wie zum Beispiel Exoskelette. Diese Assistenzsysteme werden zunehmend in Industrie- und Logistikunternehmen eingesetzt. Sie sind äußerlich am Körper angebracht und dienen als Stützstrukturen, die die Bewegungen des Arbeiters mechanisch unterstützen und verstärken. Exoskelette können in aktive und passive Strukturen unterteilt werden, je nach ihren Komponenten und Funktionalitäten. Aktive Exoskelette verfügen über mechanische Elemente und Komponenten, die zur Last- und Kraftreduktion beitragen. Dies wird beispielsweise durch eingebaute Elektromotoren und Batterien erreicht.
Passive Exoskelette
Passive Exoskelette hingegen unterstützen den Körper ausschließlich durch mechanische Komponenten wie Gewichte, Federn oder Schienen, ohne einen aktiven Antrieb zu haben. Während passive Exoskelette bereits in der Produktion bekannter Unternehmen eingesetzt werden, befinden sich aktive Exoskelette größtenteils noch in der Testphase. Dies liegt zum Teil an den deutlich geringeren Anschaffungskosten von passiven Exoskeletten, die nur einige tausend Euro betragen.
Zusammenfassung Exoskelette
Sowohl aktive als auch passive Stützstrukturen haben Vor- und Nachteile. Während aktive Exoskelette auf externe Stromquellen angewiesen sind, um die Batterien aufzuladen, sind passive Modelle nicht von externer Stromversorgung abhängig. Aktive Modelle sind oft schwerer, bieten jedoch eine deutlich höhere Unterstützung. Mit Hilfe solcher Assistenzsysteme können die biomechanischen Belastungen für die Mitarbeiter reduziert werden, was zu einer Verringerung der krankheitsbedingten Ausfallzeiten führt.
Zusammenfassung Digitale Assistenzsysteme
Die Vorteile von Assistenzsystemen im Kontext der vierten industriellen Revolution, auch bekannt als Industrie 4.0, werden beleuchtet. Er wird erläutert und hervorgehoben, wie diese Systeme die Produktivität steigern, die Zufriedenheit der Mitarbeiter verbessern und ältere oder behinderte Arbeitnehmer einbeziehen können. Es werden dabei verschiedene Arten von Assistenzsystemen, einschließlich kognitiver Systeme wie erweiterter Realität, virtueller Realität und gemischter Realität sowie physischer Systeme wie Exoskelette untersucht. Es wird erklärt, wie diese Systeme Mitarbeiter bei verschiedenen Aufgaben unterstützen können, indem sie visuelle Anweisungen und mehrsprachige Informationen bereitstellen, Montageprozesse erleichtern und Maschinendaten integrieren. Der Blogbeitrag schließt mit der Betonung der Bedeutung des Schutzes teurer Displays und Touchscreens mit hochwertigen Schutzfolien oder Hybridglas, die nicht nur ihre Lebensdauer verlängern, sondern auch die Zufriedenheit der Mitarbeiter erhöhen.
Wichtige Erkenntnisse
- Assistenzsysteme in der vierten industriellen Revolution bieten zahlreiche Vorteile, darunter gesteigerte Effizienz, verbesserte Ergonomie und die Einbeziehung älterer oder behinderter Arbeitnehmer.
- Kognitive Assistenzsysteme wie erweiterte Realität, virtuelle Realität und gemischte Realität ermöglichen innovative Interaktionen mit Maschinen und erleichtern verschiedene Aufgaben in Industrie und Handwerk.
- Digitale Assistenzsysteme können eine Vielzahl von Inhalten anzeigen, darunter Zeichnungen, Materiallisten, Arbeitspläne und allgemeine Informationen, um Mitarbeiter in ihrer täglichen Arbeit zu unterstützen.
- Schutzfolien oder Hybridglas können teure Displays und Touchscreens schützen, ihre Lebensdauer verlängern und die Notwendigkeit teurer Reparaturen reduzieren.
- Physische Assistenzsysteme wie Exoskelette bieten mechanische Unterstützung für Arbeitnehmer, reduzieren biomechanischen Stress und minimieren Krankheitszeiten.





 . A strong 256-bit encryption secures the data transfer. With our externally issued SSL certificate, we are transparent and compliant. In addition to the SSL-secured website, we take data protection very seriously.
. A strong 256-bit encryption secures the data transfer. With our externally issued SSL certificate, we are transparent and compliant. In addition to the SSL-secured website, we take data protection very seriously.
Latest comments